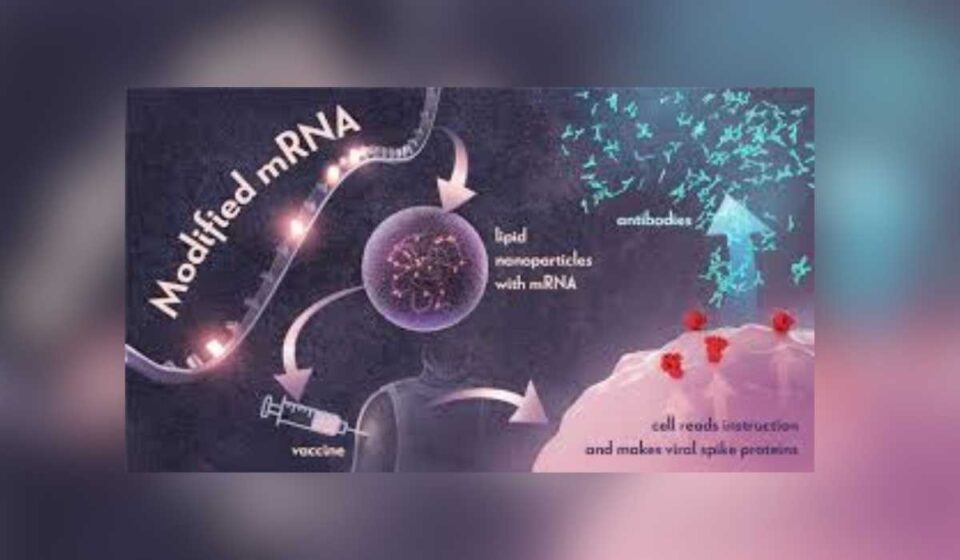
mRNA technology, which gained widespread recognition during the COVID-19 pandemic for its role in developing highly effective vaccines, is now being explored for a broader range of medical applications. Companies like Moderna and BioNTech, pioneers in mRNA vaccine development, are extending their research to tackle other critical global health challenges. The potential for mRNA to revolutionize treatments for diseases like cancer, autoimmune disorders, and rare genetic conditions has opened up new possibilities for biotech, signaling a transformative shift in medical research.
In cancer treatment, mRNA vaccines are being studied as a way to train the immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. By encoding specific proteins associated with tumors, mRNA therapies could stimulate a stronger immune response than traditional treatments. Moderna, for example, has launched clinical trials for personalized mRNA cancer vaccines that target unique mutations in individual tumors. These therapies offer the promise of precision medicine, allowing for highly tailored treatments that could significantly improve outcomes for cancer patients.
Beyond cancer, mRNA technology is also being explored for autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and lupus. In these cases, mRNA therapies could potentially modulate the immune system to prevent it from attacking the body’s own cells. This marks a significant advancement in the treatment of chronic, debilitating diseases that currently have limited therapeutic options. The flexibility of mRNA platforms allows for rapid adaptation and innovation, making it easier to develop targeted treatments for complex autoimmune disorders.
Additionally, mRNA technology holds great potential in addressing rare genetic disorders. By delivering mRNA sequences that can replace faulty genes or proteins, these therapies offer a new approach to treating diseases that were previously considered untreatable. Companies like BioNTech are at the forefront of this research, working on therapies for conditions such as cystic fibrosis and certain types of muscular dystrophy. The ability to use mRNA to correct genetic mutations could provide life-saving treatments for patients with rare diseases who currently have few options.
The economic impact of these advances is significant, with biotech companies attracting substantial investment to further their mRNA research. According to recent data, global investments in mRNA-related technologies have surged, with billions of dollars flowing into clinical trials and drug development. As mRNA therapies expand into new areas, the biotech sector is poised for continued growth, potentially reshaping the healthcare industry and offering innovative solutions to some of the world’s most pressing medical challenges.