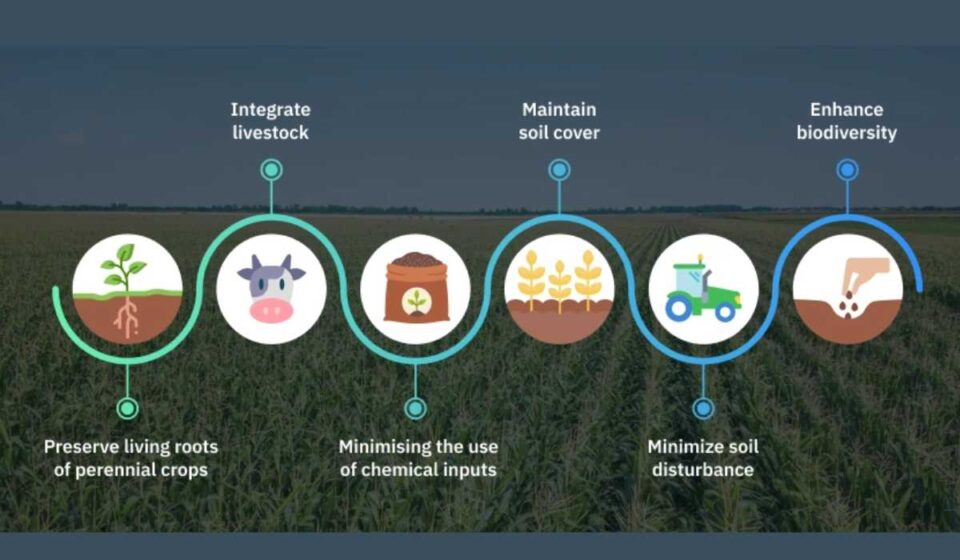
Regenerative agriculture is a holistic farming approach that emphasizes the restoration of soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem balance. Unlike traditional farming methods that often deplete natural resources, regenerative agriculture aims to enhance soil fertility, increase biodiversity, and sequester carbon, thereby mitigating climate change. This approach not only benefits the environment but also improves the resilience and productivity of agricultural systems, making it an attractive option for businesses in the agriculture and food industries.
Several companies are leading the way in adopting regenerative practices, showcasing the potential for a sustainable and profitable future. For instance, some large food corporations are partnering with farmers to implement cover cropping, rotational grazing, and reduced tillage techniques. These practices help improve soil structure, increase water retention, and reduce the need for chemical inputs, leading to healthier crops and ecosystems. Additionally, smaller startups are pioneering innovative regenerative methods, such as agroforestry and no-till farming, which further demonstrate the diverse applications and scalability of this approach.
Despite the promising benefits, regenerative agriculture faces challenges to widespread adoption, including the need for education, financial investment, and supportive policies. Farmers may be hesitant to transition due to the upfront costs and the time required to see tangible benefits. However, as consumer demand for sustainable and ethically produced food grows, businesses have a unique opportunity to lead the shift towards more sustainable farming practices. The future of regenerative agriculture holds great potential to transform the food industry, offering a pathway to sustainability that aligns environmental health with economic viability.